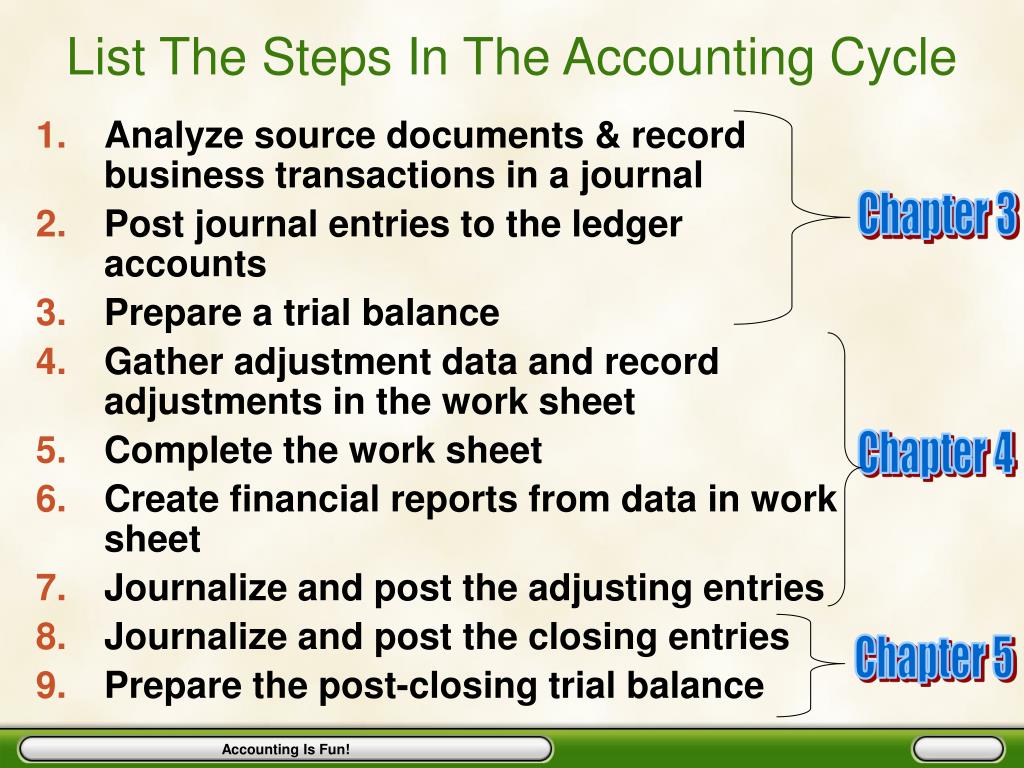
These steps ensure that a company’s financial statements are accurate, up-to-date, and in compliance with regulatory requirements. These journal entries are known as adjusting entries, which ensure that the entity has recognized its revenues and expenses in accordance with the accrual concept of accounting. The accounting cycle is the backbone of financial management and reporting. From recording transactions to preparing financial statements, each stage of the accounting cycle plays an important role in making sure a business’s financial information is accurate and up to date. Here’s an in-depth look at the accounting cycle, including the eight primary steps involved and how accounting software can help. It starts with recording all financial transactions throughout that accounting period and ends with posting closing entries to close the books and prepare for the next accounting period.
Record transactions in a journal.
It’s worth noting that some businesses also have internal accounting cycles that have a shorter accounting period. These internal accounting cycles follow the same eight accounting cycle steps and can last anywhere from one month to six months. The accounting cycle is a holistic process that records a business’s transactions from start to finish, helping companies stay organized and efficient.

Ensures financial statement accuracy and compliance
The general ledger comprises of multiple ledger accounts, which are the primary components of a business’s financial statements. Each ledger account pertains to a specific aspect of the business, such as assets, liabilities, revenues, or expenses. In conclusion, initiating transactions in the accounting cycle involves recognizing transactions, creating journal entries, and maintaining documentation. This process ensures a clear, well-organized, and accurate representation of a company’s financial activity, laying the foundation for subsequent steps in the accounting cycle. Understanding the accounting cycle is vital for business owners and professionals in the accounting field.
Free Course: Understanding Financial Statements
- Another perk of using accounting software is the reporting functionality that allows you to generate essential reports and analyze your company’s financial health easily.
- Regardless, most bookkeepers will have an awareness of the company’s financial position from day to day.
- Missing transaction adjustments help you account for the financial transactions you forgot about while bookkeeping—things like business purchases on your personal credit.
- Still, businesses need to fill out expense reports to track monies paid.
- Depending on each company’s system, more or less technical automation may be utilized.
The accounting cycle plays a crucial role in financial reporting by providing a structured and systematic process for recording, organizing, and presenting a company’s financial information. It ensures that financial statements are accurate, consistent, and comply with applicable accounting standards. The accounting cycle aids in effective decision-making, internal and external reporting, and regulatory compliance. In the posting process, transactions from the journal are organized and categorized into their respective ledger accounts.
Generating unadjusted trial balance report
Or, if you receive a payment, your sales revenue is credited while your bank account is debited. If you need a bookkeeper to take care of all of this for you, check out Bench. We’ll do your bookkeeping each month, producing simple financial statements that show you the health of your business.
Troubleshoot errors quickly
When you make a sale, the accounting software automatically adds the transaction to the revenue account and updates the income statement. You can also link your ERP and other systems so the accounting software how to use the excel timevalue function can record and monitor expenses. Accounting software can help avoid the hassle of correcting these errors because it checks the amounts and whether debits and credits are equal when you post journal entries.
Essentially, the accounting cycle represents a carefully orchestrated series of steps that converts raw financial data into meaningful and comprehensible reports. For example, if the bookkeeper had debited cash by $100 and credited customer A’s account by $1,000, the credit and debit balances wouldn’t match. The bookkeeper will need to change the amount in the journal entry or pass an adjusting entry to fix the error. The first step in the accounting cycle is to identify your business’s transactions, such as vendor payments, sales, and purchases. It’s helpful to also note some other details to make it easier to categorize transactions.
The next step of the accounting cycle is to organize the various accounts by preparing two important financial statements, namely, the income statement and the balance sheet. The income statement lists all expenses incurred as well as all revenues collected by the entity during its financial period. These expenses and revenues are compared to reveal the net income earned or net loss sustained by the entity during the period. This step summarizes all the entries recorded by the business during a particular period, which is generally the financial year of the entity. It is done by preparing an unadjusted trial balance – a list of all account titles along with their debit or credit balances.
We’re going to go over all of the steps and provide examples of what each step would look like. The operating cycle can be expressed in a formula as the sum of the financial analysis ratios for days’ sales outstanding and the average collection period. Understanding the operating cycle in your business is essential for cash flow management. For example, a personal loan made by a business owner that does not have anything to do with the business shall not be recorded in the books of the business. When the owner buy a personal car, it should also not be recorded as an asset of the business.
